Page speed is the speed at which a user is able to access and interact with a website’s content. Major tech companies invest heavily in page speed because it is associated with lower bounce rates and higher conversions. For search engine optimization purposes, page speed is important because it is one of Google’s leading page ranking factors.
When users enter keywords into Google’s search engine, Google then crawls the internet for the sites that best match the user’s request. The quicker Google is able to access your site’s content, the more likely it will appear higher in search results. While this subject may sound technical, there are a few basic steps one can take to improve their website’s page speed. In this post we will outline the best ways you can enhance page speed to improve your website’s search engine ranking.
To test your site’s current page speed, head to over to a site like GTMetrix, Pingdom, or Google’s PageSpeed Insights; you can enter your URL and receive a report on how quickly your website’s content is accessible. You will notice companies such as Google have extremely rapid response times — if you want your site to appear in top search results you should employ some of the following techniques to improve page speed.
Reduce HTTP Requests
Reducing the amount of HTTP requests is one of the first actions a site manager should take to enhance page speed. There are a few ways to limit requests:
Minify Your JavaScript and CSS
Minifying your code is the process of stripping away any unnecessary data that has no impact on the code’s functionality. In doing so, you reduce the amount of data a browser interacts with, which in turn improves your page’s loading time. You can analyze the code yourself to find redundancies, or you can use online tools to minify your code for you. For JavaScript, the Closure Compiler is a popular minifying tool you can access online. For CSS, CSSNano is the most effective minifying tool on the market.

Compress Site Files
This is one of the first actions a site manager should take to enhance page speed. When a user accesses your site, a large amount of the response time is derived from downloading all the data your site contains. You can help reduce the amount of HTTP requests by simplifying your page, but this can be hard when you’re trying to create a responsive site. Compressing files on your site reduces the time it takes for the browser to download your page. This is one of the easiest ways to increase your page speed.
Use the Gzip command to compress text files such as HTML. This will drastically reduce your page’s response time. Most images and PDFs are already compressed — avoid further compressing them as it can create complications with the files. The only disadvantage in using Gzip to compress files is its incompatibility with older browsers such as Internet Explorer. But given how few people use outdated platforms, Gzip’s benefits far outweigh the costs. If you’re not hosting on your own server, you will want to reach out to your hosting service to enable Gzip compression.
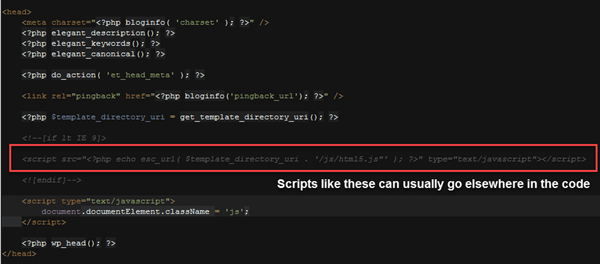
Remove Javascript Files From Head Section
You can increase a page’s speed by removing the Javascript from the <head> section and placing it at the bottom of your page. This allows the HTML to render prior to the Javascript. This is advantageous because Javascript doesn’t allow further rendering of pages prior to all files being downloaded.
Tools For Page Speed Optimization
For WordPress users, the W3 Total Cache Plugin can help reduce HTTP requests by automatically caching files, feeds, and objects on your website. In addition, it can automatically minifies your CSS and Javascript code to help reduce loading times. It is one of the most recommended WordPress Performance Optimization Tools on the market.
Tip: Do not make any major changes without backing up your site first. One small change to a line of code can break an entire site. It could then be timely and costly to fix it.
Image Optimization
Images are responsible for most of the data storage on your web page. In comparison, text takes up a very small portion of the downloaded bytes on your site. For this reason it is crucial that images are optimized to be accessible and downloadable as efficiently as possible. First, delete any images on your site’s pages that offer no benefit to the visitor. Just because something might look cool, doesn’t mean it’s beneficial, and could detract from the user experience. Second, change still images from GIFs to PNGs or JPGs as this will often increase the speed at which the images are downloaded.
In addition, run an optimizer on all of your site’s images. Popular image optimizers include Pngcrush and Kraken. These services can compress images down without compromising image quality. Additionally, there are plugins for WordPress that can optimize your images automatically, so you don’t have to run them manually.
For example:
The total value of the images in this article before optimization was about 1,300 kilobytes.
The current value of all the images in this article after optimization is about 1,100 kilobytes.
This is a savings of about 200 kilobytes, which is 15.4%.
On its own, it may not seem that significant, but when you start to multiply it, it really adds up. If this article gets 100,000 views, then that’s a bandwidth savings of around 20 gigabytes. To add to the point, some people may not have quick internet connections, so every kilobyte counts.
Depending on many factors, such as how much color is in an image, what file format it is, what the dimensions are, how many images are on a page, etc, you may see a greater or lesser amount of savings.
Tip: It is also important to name your images correctly and purposefully; they factor into your SEO keyword rankings. Some site traffic comes through Google Images, so make sure users will be able to find you that way.
Avoid Redirects
You can easily find out if your site is unnecessarily redirecting by running your URL through Internet Officer’s Redirect Checker. We expand into different aspects of redirecting in one of our previous posts, including what you need to do to your .htaccess file. If your site is relatively new, there is a high chance that it is not currently redirecting — but there are still a few ways your site may be redirecting without you realizing.
Redirecting an old URL to a new URL may be slowing your page speed. With a site audit, you can determine all URLs that aren’t correct in order to fix them, so you can avoid the extra time it takes to redirect. In addition, not having a trailing slash (/) after a URL causes a page to redirect to find the appropriate URL.
For example:
https://donovic.com is not the same as https://donovic.com/

As you see, the trailing slash may seem minuscule and not important, but just make it a habit to fix it if you see it. You’ll thank yourself in the long run.
Another way that your site may be redirecting is through your backlinks. You may have updated your URLs, and a site may be pointing to your old link. Or, you may have switched to HTTPS. Whatever the case, a backlink analysis could give you the insight you need to see what sites are linking to you. From there, you can create a strategy for reaching out and getting them to change that link. It’s not only a win for the site that links to you, but it’s a win for you, since the link is now a direct path to your site.
Upgrade Your Hosting
Hosting plays a small roll in your website’s speed but shouldn’t be ignored, especially if you experience high volumes of traffic. Free hosting or low-fee hosting services account for the majority of hosted websites on the internet. If you want your site to be able to handle high volumes of traffic quickly, consider upgrading your hosting. While there are associated costs, purchasing a dedicated server through a hosting company ensures that you are not sharing resources with other websites. This can help enhance server response times. Next, we’ll go through the pros and cons of having your own server, using a dedicated server, or using shared hosting.
Having Your Own Server
Pros
- You have control of every aspect of your hosting.
- If you need more resources, you can easily purchase them yourself and add them.
Cons
- The biggest pro is also the biggest con – it’s up to you to implement or fix everything. This can add up to lots of time and money spent.
- The stress of power outages or loss of internet service at your home or business.
- Must be knowledgeable in setting up and maintaining a server.
- Many internet service providers (ISPs) may consider this a no-no. Check with your ISP’s terms and conditions before implementing your own server.
Using A Dedicated Server
Pros
- That server is only hosting your site, which means you have your own IP and your own bandwidth allocation without having to worry about other sites.
- It will be more secure. If a shared server gets hacked, it could affect all sites on that server – this ensures only one site would be affected by a hack.
Cons
- Cost. This can get very expensive, very quickly. Plans usually start at around $100/month and depending on your needs, can go up exponentially.
- There’s a large learning curve. Less so than setting up your own server, but it’s not as easy as buying hosting and installing your site on it.
Using Shared Hosting
Pros
- Very affordable. Some registrars offer first year deals that make it very enticing for new site owners. Typically, a whole year’s worth of shared hosting costs less than one month of dedicated hosting, making it an affordable option for sites and businesses just starting out.
- It’s super convenient. You’ll usually have cPanel pre-installed, which allows you to easily install WordPress or the CMS of your choice via Softaculous, a web app installer. This is just the tip of the iceberg on what cPanel offers – that’s a whole separate post.
Cons
- Nothing is really in your control. Sometimes a feature may not be available on your server, and there’s nothing you can do about it.
- If a site on the server is compromised by malicious hacking or scripts, your site could be at risk as well.
- If a site on the server gets a spike in web traffic, your site’s performance and loading time could suffer greatly.
- You don’t get your own IP address.
Verdict
There are more factors that determine page speed, but this list should give you a great start on making your site quicker. If you suffer from a slow site, you now know that it doesn’t have to be that way. It may be as simple as installing a plugin to get the greatest gains, or it may be something a little more painful – such as switching up your server.
Investing time in improving your page speed is crucial in sharpening your website for SEO. Enhancing your website’s speed should be part of an all encompassing SEO strategy that includes other mechanisms such as link building, content strategy, and a host of other page ranking methods. Work to improve your page speed using the tips we’ve outlined in this article — it takes time but it’s worth it! After you make alterations, make sure to track your site analytics. If you have an all encompassing organic SEO strategy, there’s no doubt that you’ll see a boost in site visibility.

